VoIP vs. Landlines: Why the Internet-Based Phone Wins Every Time

But it’s no shock that telephony now comes in far more options than just the traditional business landline. The most popular is VoIP (voice over internet proxy), an option that relays your voice calls entirely through the internet. While exciting to some, VoIP phone lines also present a dilemma to those used to an analog phone system. Is it worth keeping that old setup, or is an upgrade in order?
Weighing the question of landline vs. VoIP telephony is critical to building effective business communications — but frankly, deciding is a lot simpler than you may think. Read on to learn the differences between the two, and what makes a VoIP phone line the consistently better option.
Defining VoIP vs. Landline
But before we compare landlines to VoIP in detail, let’s take a moment to consider how the two actually work.
What is a landline phone?
A landline phone connects to an analog phone line to make and receive calls. This means the phones are physically connected to copper wires or fiber cables run from phone outlets to external lines. All these extensions serve to connect the phones to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), or the wider network of physical telephone lines.
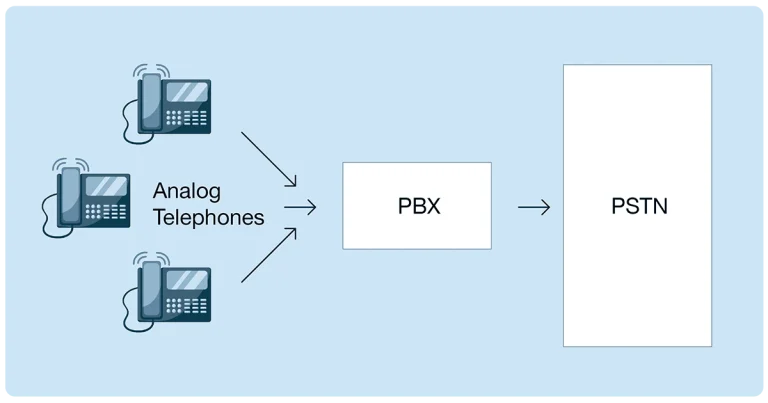
So going with a landline means using an analog phone system in the most basic sense: a physical telephony connection that relies entirely on cables run inside your organization’s property and the cables from public infrastructure.
What is VoIP?
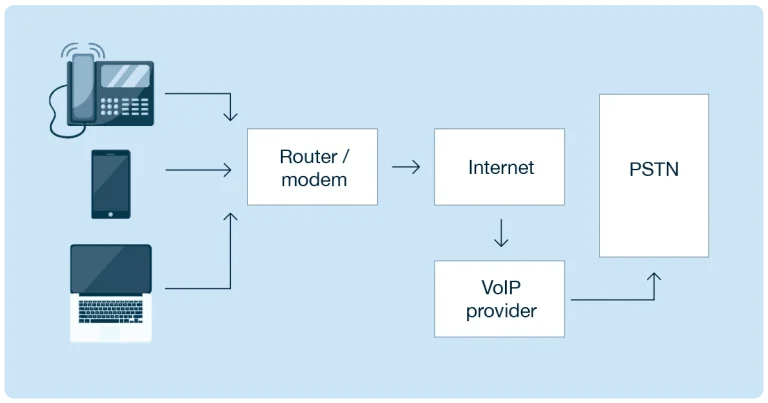
VoIP refers to internet-based phone systems. Rather than using analog phone lines, here calls are connected via your internet service, whether that’s through ethernet cables, Wi-Fi or mobile data.
Aside from this difference in connection, however, VoIP completes calls just the same way as any business landline would, and is completely compatible with analog telephony. An internet phone line will still have a phone number that any other device can dial and reach. It’s just that, since they’re on the internet, VoIP phone users will complete that call through a web connection.
Comparing VoIP vs. Landline
So, how do analog phones and internet-based phones measure up in actual use? Does being connected to the internet really give VoIP a leg up over landlines?
If you’re looking for a quick answer, the reality is VoIP is easily the stronger offering. In every possible case, it’s wiser to go with a web-powered communications system than analog phones solely because of the added functionality. (The fact that VoIP is also cheaper and simpler to manage doesn’t hurt things either.)
But every case has exceptions, and yours might be unique. So consider these points for comparing landlines to VoIP to choose what is best for your business.
Features
How do the two mediums compare in functionality?
Landline
Unlike VoIP, landline phones have a relatively short features list, as by design they aren’t built to do much beyond make and receive calls. Of course, by now it’s also standard to have voicemail as part of the system, so most landline connections will also enable your organization to save voice messages when calls come in after hours.
In some cases, landline-based analog phones can also provide Interactive Voice Response (IVR) menus, allowing callers to connect to a given department or extension without a human attendant. However, this feature is typically time-consuming to implement on analog connections, and will also usually require on-site hardware to power it.
VoIP
VoIP, meanwhile, handles both IVR and voicemail with no additional on-site hardware. But that’s just scraping the surface when it comes to VoIP features — frankly, those switching from landline to VoIP are typically doing so for the extra functionality.
And that shouldn’t be surprising, considering VoIP also offers:
- Voicemail transcription
- Autoattendants
- Number porting
- Custom call flows
- Call data and analytics
- Blocked number lists
- Spam prevention
- Call recording
- Ring groups
Result?
Purely in terms of functionality, VoIP wins over landline in every single category. Even if you have zero interest in features like chats or video meetings, the sheer scope of features, customizability and flexibility in VoIP makes it far and away the better business option.
Deployment
So, what about how easy it is to get each of these technologies set up?
Landlines
The most common reason to use an analog phone system today is if your property already has a landline connection built in. However, if you don’t currently have a business landline connection, be warned that installing one will without exception be time-consuming and expensive.
Even today, there’s no way to add cabling other than to install it — and doing that means physically running cables through walls so they can reach a physical PBX and phones. However experienced your technician is, this process will always take several hours at minimum. You’ll also need more cable work performed if you want to change the hardware or number of extensions for your system.
VoIP
VoIP is again a clear winner in this category, because in any deployment of IP telephony the installation will at least be easier than landline.
Setting up VoIP phone lines rarely takes more than an hour. A big reason why is that modern VoIP systems seldom use any hardware aside from your choice of end-devices, which can be anything from compatible desk phones to your current laptops. As a result, all technicians need to set up your system is work through its associated software and connect you to the cloud.
In many cases, your technicians don’t even need to be on-site to handle the installation. Because they work through the internet, VoIP phone systems can even be set up remotely through computers. Adding or removing users is as easy as changing some settings in your configuration, meaning both growth and downsizing can be accommodated quickly and cheaply.
Result?
Again, there’s no real competition here. To whatever extent you need to set up or change a telephony installation, it will always be easier with a VoIP setup.
Price and Scalability
How expensive is setting up these tools? What about changing them further down the line?
Landlines
If you already have a landline connection, then obviously you’ll save a decent amount of money simply from not having to set one up. Payment outside of that will cover necessary hardware and the wired connection costs, which are usually handled at a flat rate with more charges for long-distance or international numbers.
Though that may seem cheap on the face of it, bear in mind adding users to your landline PBX will cost you significantly thanks to the time and cabling they’ll require. Much the same goes if you want to add features onto your business landline, since it will need extra hardware to do so.
VoIP
VoIP will cost you on a monthly per-user basis, ideally letting you mix and match your licensing types in the process. This ensures that, although you’ll be paying more for additional features, you’ll only be paying for ones you actually use.
As far as hardware goes, VoIP gives you tremendous room for customization. You’ll be able to purchase an on-site PBX if you prefer, but most VoIP users skip the extra hardware altogether by simply going to the cloud. With cloud-based hosted setups, the only devices you’ll need are desk phones or your existing lineup of smartphones and laptops, which can connect to your PBX in the cloud anywhere they receive internet.
Result?
Realistically, there aren’t many scenarios where a landline connection will cost less than a VoIP phone line, especially in the long term. Not only are subscription costs for VoIP cheaper all while eschewing the need for hardware, VoIP installations are typically fast and completely free. Plus, any changes to your VoIP system can be made at little to no extra cost.
Reliability
How well can you trust these tools to keep you connected?
Landlines
Business landline systems traditionally have a leg up in this regard, as the physical phone connections they use rarely experience outages outside of severe weather events. The quality of landline calls is also typically good no matter what your setup, since your calls will still travel over the same PSTN cabling.
VoIP
While VoIP and internet phone lines are also reliable, just how dependable they are can vary. The biggest factor is your own internet connection: to support high-quality calls, especially multiple ones at once, you’ll need consistently high upload and download speeds. That said, internet-based phone calls are designed to respond to sudden changes in internet speeds, so with a good choice in system, you shouldn’t expect drastic shifts in sound quality or outright dropped calls.
But suppose the internet at your organization goes out — does that mean your VoIP system will go down? Not necessarily.
These days, any effective VoIP system will also feature ways to get back online in the event of an outage. Most commonly, you can simply connect your internet phone line to mobile data, which will keep your phone lines active just as readily. And even if 4 or 5G is also a no-go, most VoIP systems also feature failovers that route incoming calls elsewhere in the event of an outage, such as to voicemail or an alternate location.
Result?
Although landline phones are as a whole slightly less prone to outages than VoIP, remember that there are numerous ways around this issue on an internet phone line. If 100% phone uptime is a must for your organization, talk to your technician about it, and you’ll easily find a solution that’s right for your setup, such as additional network connection methods or even an extra ISP.
VoIP vs. Landlines: Which Is Right for Me?
Put bluntly, it’s VoIP. (And, really, were you expecting anything else?)
Yes, business scenarios always vary when it comes to considering landlines vs. VoIP. You may very well not have the fastest internet, and you may even have an existing business landline that you’d just need to contact a carrier to activate. Internet phones may even seem like a new, hard-to-understand technology that has more functions than you really need.
Even in those cases, internet-based phone systems still come out on top every time. The most basic of VoIP phone lines — that is, ones that do little more than place and receive calls — will do everything a landline connection can, for one thing. But more importantly, they’ll also be cheaper to use and maintain, far simpler to expand and significantly more capable of improving your business communications.
Although when compared to VoIP, landlines may in some cases have a slight edge in reliability, internet phone lines still provide far more in usability for a very comparable (if not significantly cheaper) price. Wherever your organization is at right now, a VoIP system will both fit those current needs and be readily able to change to meet whatever future requirements you may end up having.


